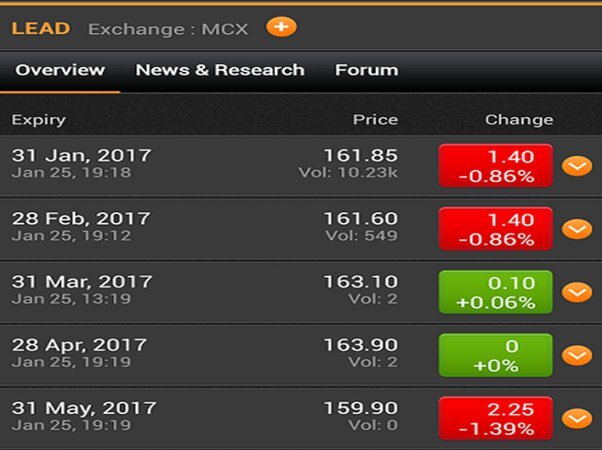
Description
Trading options on the Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX) allow investors to engage in sophisticated trading strategies that can potentially enhance returns and manage risk. Options trading involves using contracts that give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell underlying commodities at a predetermined price before or on a specified date. In the MCX market, traders can utilize various options tailored to their market outlook and risk tolerance. Understanding and implementing effective MCX Option Trading Strategies can help traders navigate the complexities of the options market, optimize trading decisions, and achieve their financial goals.
Critical Components of MCX Option Trading Strategies
- Understanding Option Basics:
- Calls and Puts: Options come in two forms: calls, which give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset, and puts, which give the holder the right to sell it.
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the underlying commodity can be bought or sold.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires.
- Premium: The cost of purchasing the option contract.
- Basic Options Strategies:
- Covered Call: This strategy involves holding a long position in an underlying commodity and selling a call option on that commodity. It generates additional income from premiums while potentially capping upside gains.
- Protective Put: This strategy involves holding a long position in an underlying commodity and buying a put option as insurance against potential price declines. It provides downside protection while allowing for upside potential.
- Long Call: Buying a call option with the expectation that the underlying commodity’s price will rise significantly. This strategy benefits from an increase in the commodity’s price above the strike price.
- Long Put: Buying a put option with the expectation that the underlying commodity’s price will fall significantly. This strategy profits from a decline in the commodity’s price below the strike price.
- Intermediate Option Strategies:
- Straddle: This strategy involves buying a call and a put option on the same underlying commodity with the same strike price and expiration date. It is used when expecting significant price movement but uncertain about the direction. It benefits from high volatility.
- Strangle: Similar to a straddle, the call and put options have different strike prices. This strategy also benefits from significant price movements in either direction, with a lower initial cost than a straddle.
- Butterfly Spread: This strategy involves buying and selling multiple calls or options at different strike prices to create a position with limited risk and profit potential. It is used when expecting minimal price movement and aims to profit from small price changes.
- Iron Condor: This strategy involves selling an out-of-the-money call and put option and buying a further out-of-the-money call and put options. It is used to profit from low volatility and price movement with limited risk and reward.
- Advanced Option Strategies:
- Vertical Spread: This strategy involves buying and selling call or put options with the same expiration date but different strike prices. It can be bullish (bull call spread) or bearish (bear put spread) and is used to profit from moderate price movements.
- Calendar Spread: This strategy involves buying and selling options with the same strike price but different expiration dates. It is used to profit from time decay and volatility changes.
- Diagonal Spread: This strategy involves buying and selling options with different strike prices and expiration dates. It combines vertical and calendar spread elements and manages risk and profit from price movements and time decay.
- Risk Management and Position Sizing:
- Risk Assessment: Risk management is crucial in options trading due to the complexity and leverage involved. Traders should assess the potential risks of each strategy, including maximum loss, breakeven points, and likely gains.
- Position Sizing: It is essential to determine the appropriate size of each trade based on risk tolerance and overall trading capital. Proper position sizing helps manage risk and avoid excessive exposure to any single trade.
- Real-Time Market Analysis and Insights:
- Market Trends and Indicators: Stay informed about market trends and indicators that impact options pricing, such as commodity price movements, economic data releases, and geopolitical events.
- Volatility Analysis: Understand how volatility affects option prices. Higher volatility generally increases option premiums, while lower volatility decreases them.
- Execution and Monitoring:
- Order Types: To manage trades effectively, utilize different order types, such as limit orders, stop-loss orders, and trailing stops.
- Monitoring Positions: Continuously monitor open positions and adjust strategies based on market conditions and underlying commodity price changes.
- Educational Resources and Tools:
- commodity’stforms: To enhance trading performance, use advanced trading platforms that offer real-time data, sophisticated charting tools, and automated trading signals.
- Educational Materials: Access educational resources, including webinars, tutorials, articles, and courses, to deepen your understanding of options trading strategies and techniques.
Benefits of MCX Option Trading Strategies
- Enhanced Profit Potential: Utilize various strategies to capitalize on market conditions and price movements.
- Risk Management: Implement strategies, such as covered calls and protective puts, to manage risk and protect capital.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Adjust strategies based on market outlook, volatility, and individual trading goals.
- Cost Efficiency: Benefit from strategies allowing lower upfront costs, such as strangles and spreads.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Gain insights from expert analysis, real-time data, and advanced trading tools to make informed trading decisions.